Assignment:-02
1. Differentiate while from do-while.
Ans:-
Ans:-
2. Define user defined data types .
Ans:-User-Defined DataTypes:
The data types that are defined by the user are called the derived datatype or user-defined derived data type.
These types include:
These types include:
- Class
- Structure
- Union
- Enumeration
- Typedef defined DataType
Below is the detailed description of the following types:
- Class: The building block of C++ that leads to Object-Oriented programming is a Class. It is a user-defined data type, which holds its own data members and member functions, which can be accessed and used by creating an instance of that class. A class is like a blueprint for an object.Syntax:
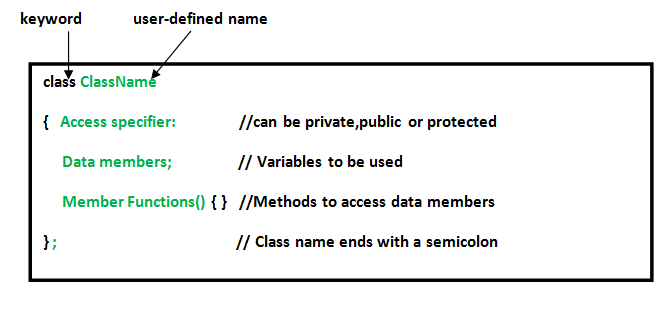 Example:Output:
Example:Output:
Geekname is: GeeksForGeeks
- Structure: A structure is a user defined data type in C/C++. A structure creates a data type that can be used to group items of possibly different types into a single type.Syntax:
struct address { char name[50]; char street[100]; char city[50]; char state[20]; int pin; };Example:Output:
10, 20
- Union: Like Structures, union is a user defined data type. In union, all members share the same memory location. For example in the following C program, both x and y share the same location. If we change x, we can see the changes being reflected in y.Output:
After making x = 2: x = 2, y = 2 After making Y = 10: x = 10, y = 10
- Enumeration: Enumeration (or enum) is a user defined data type in C. It is mainly used to assign names to integral constants, the names make a program easy to read and maintain.Syntax:
enum State {Working = 1, Failed = 0};Output:
2
- Typedef : C++ allows you to define explicitly new data type names by using the keyword typedef. Using typedef does not actually create a new data class, rather it defines a name for an existing type. This can increase the portability(the ability of a program to be used across different types of machines; i.e., mini, mainframe, micro, etc; without much changes into the code)of a program as only the typedef statements would have to be changed. Using typedef one can also aid in self-documenting code by allowing descriptive names for the standard data types.Syntax:
typedef type name;
where type is any C++ data type and name is the new name for this data type.
This defines another name for the standard type of C++.Example:Output:
c


 Rajnish kumar is the CEO/founder of
Rajnish kumar is the CEO/founder of
0 comments:
Post a Comment